AI factory
ECN Automation as a leader in automation process with experience in different sectors such as Mining, Food and Beverages, Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, Manufacturing among many more, can help you improve the Process Control of your plant by applying Artificial Intelligence (AI).
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning or automatic learning is a method of creating Artificial Intelligence, which specializes in statistical techniques for programming algorithms by which "machines learn" to perform tasks, ranging from predicting a machine failure or the prediction of variables that cannot be measured by conventional instrumentation, up to the recognition of objects within images and the understanding of human language.
Classification of ML algorithms by their learning paradigm
They are called unsupervised learning algorithms when the algorithm is trained only with the input variables, but its outputs and results have not been categorized and it is the algorithm’s responsibility to perform this categorization. On the other hand, they are called Supervised learning algorithms when they are configured for their training both their input variables (called explanatory variables) and their output variables (experimental variables).
Classification of ML algorithms by type of variable to predict
When the variable to be predicted is a category (a color, a size, a type of animal or thing), a classification algorithm must be applied and when the variable to be predicted is a number, a regression algorithm must be applied.
Regression algorithms
Classification Algorithms
Selection of the most optimal ML algorithm for each application
A methodology must be applied to select the algorithm based on the problem and the data. The selection will depend on the quantity and quality of data, the quantity of variables, etc.
How we implement Machine Learning to optimize processes
ECN Automation can implement ML applications to optimize processes under these two architectures:
1. ML Edge Module
For the implementation of applications that are executed in a system embedded in compact electronics, which can be directly integrated into DCS.
2. ML Edge Servers
For the implementation of applications in plant servers which use OPC servers to connect to the DCS or directly to historization systems such as PI System, Historian, etc.
ML applications integrated to process control
Machine Learning (ML) Edge Module allows you to accelerate the implementation of your first artificial intelligence projects, since it integrates to the data source (DCS) without using your plant’s IT infrastructure thus not being subject to cyber security restrictions that imply running your ML applications on the cloud or on your local Edge Computing local infrastructure.
This Machine Learning module connects directly to the plant’s control system (DCS) through an industrial network, using a gateway that works as a physical barrier between the DCS and the Machine Learning Edge module as shown in the following architecture:
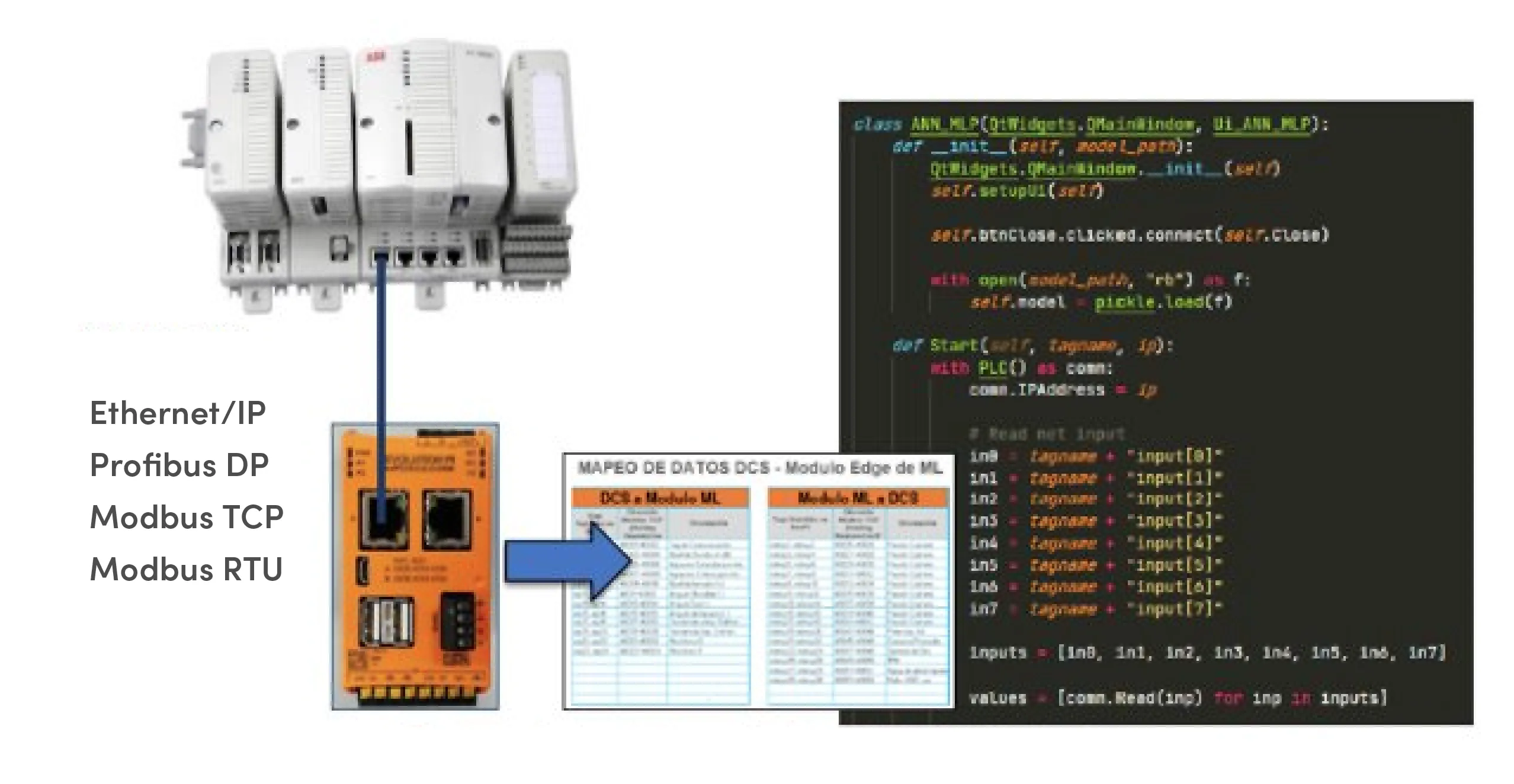
Machine Learning module integration architecture.
Local ML Server - The ML Modules manager for a distributed architecture
The local ML server is used for the development of advanced analytics applications that use your historical data, these applications have the focus of improving the operation and maintenance management of the plant and on the other hand these ML applications are directly integrated into the Plant Process Control.
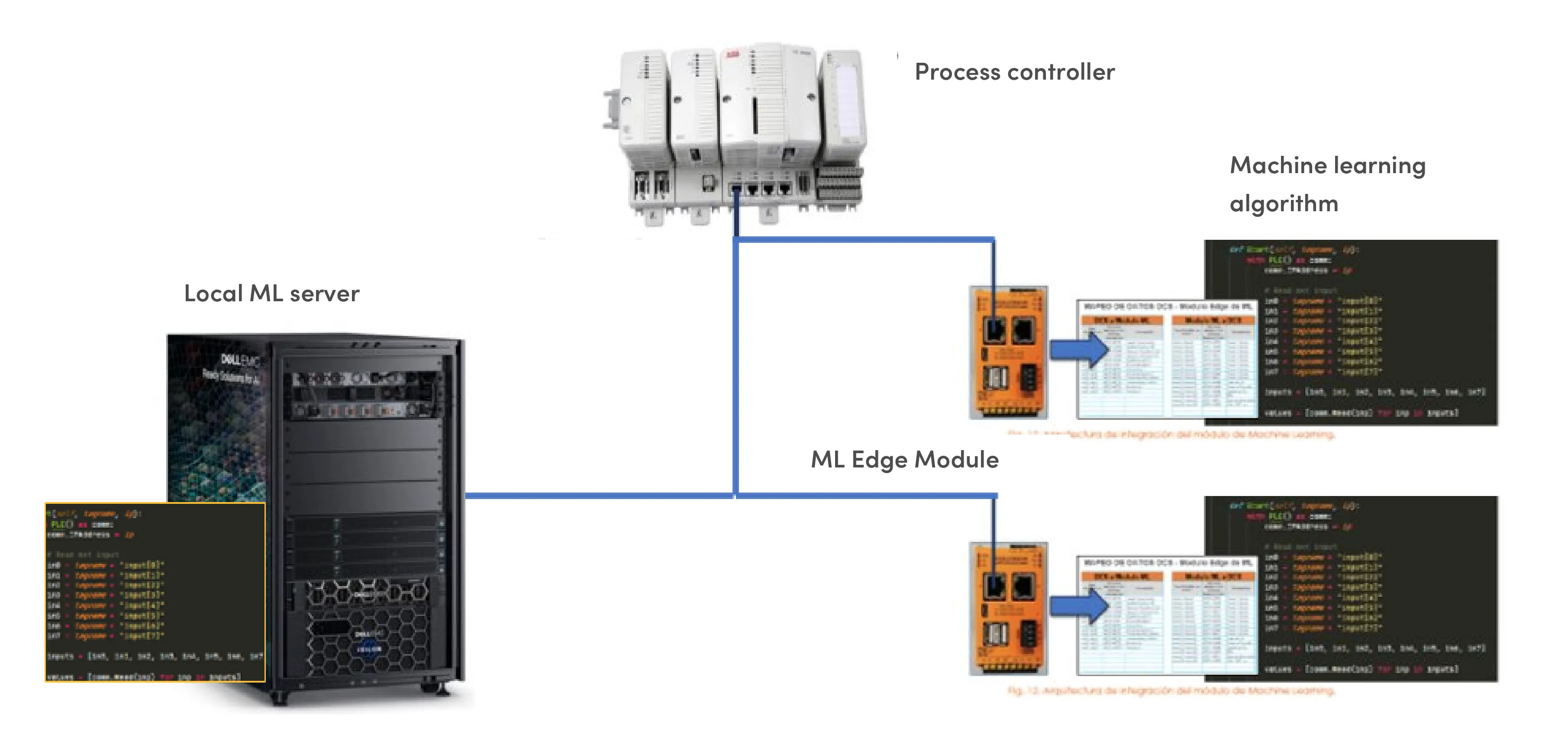
ML module integration architecture to a local server for configuration and updating of models.
ML applications in mining
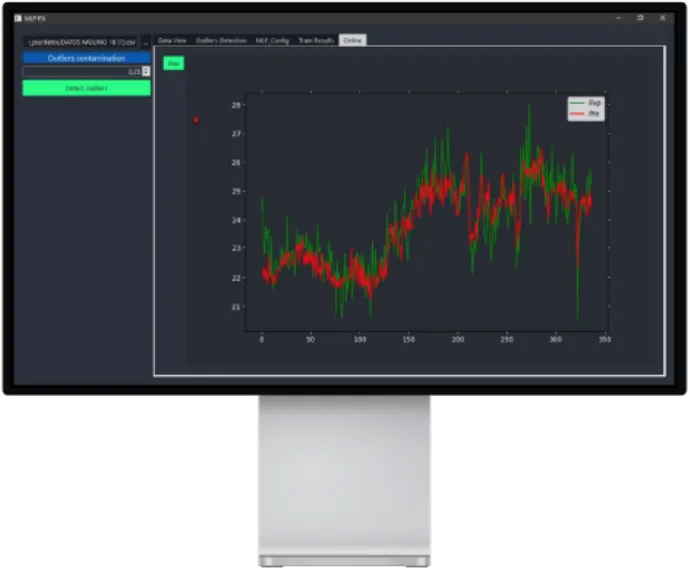
SAG Mill Operational State Detection based on Neural Networks.
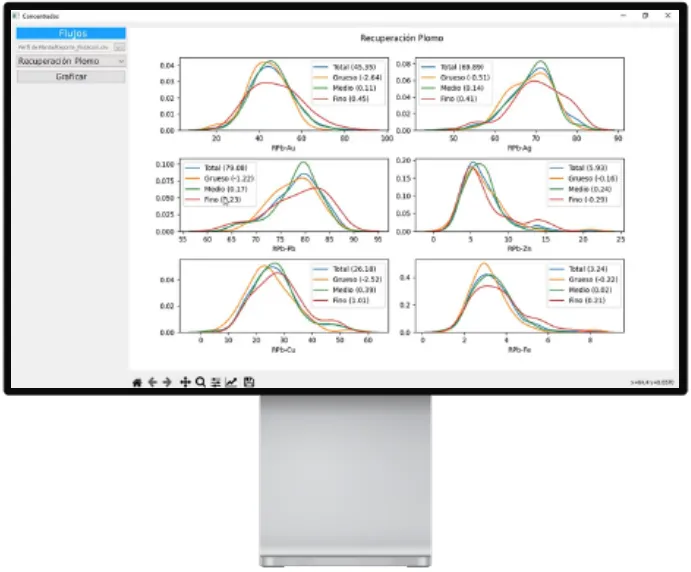
Plant profile, using descriptive analytics of the recovery and degree of concentrate for the different particle sizes
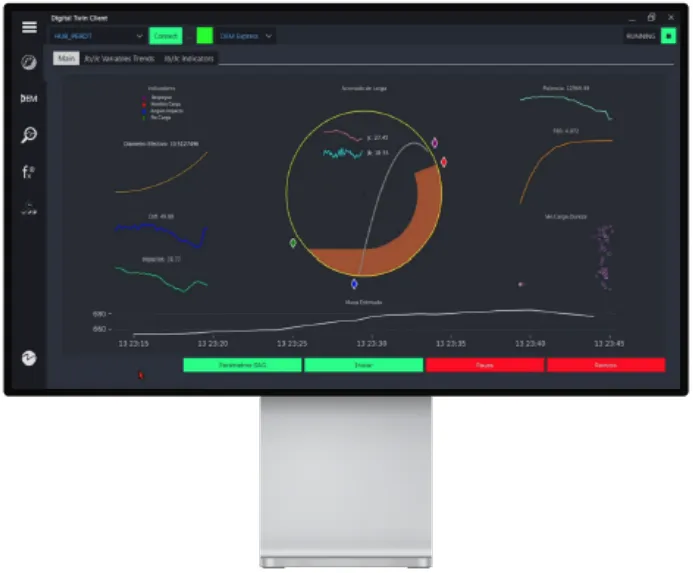
Prediction of the Jb / Jc of a SAG Mill using the C-Morrell optimization model.
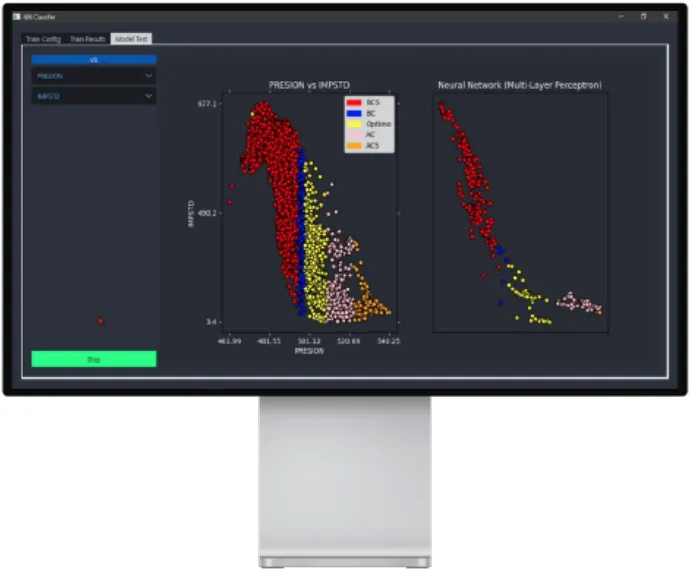
Particle size prediction in cyclone overflow based on Neural Networks.
Neural Networks
It is a simplified model that emulates the way the human brain processes information: It works by combining a large number of interconnected processing units that look like abstract versions of neurons.
Practical examples:
Benefits