Wastewater treatment
Wastewater is generated as a result of human activities, such as municipal, agricultural or industrial waste, which can have considerable concentrations of organic matter, industrial waste, detergents, fats, agricultural and livestock waste, toxic substances, among others.
Wastewater treatment is regulated by environmental laws and its compliance is mandatory for the return of water with the characteristics required by nature for its disposal in rivers and lagoons.
This type of water can be treated locally where it is produced, for example, gray water that is treated and reused directly at the source that produces it, in addition, primary treatments can be carried out by installing primary cleaning processes, while that in places with high population densities the method to treat them consists of capturing wastewater through the sewage network to be taken to the city's treatment plants.
Wastewater treatment includes a series of physico-chemical and biological processes that aim to eliminate the concentrations of contaminants present in the resource so that it can be reused.
Wastewater treatment
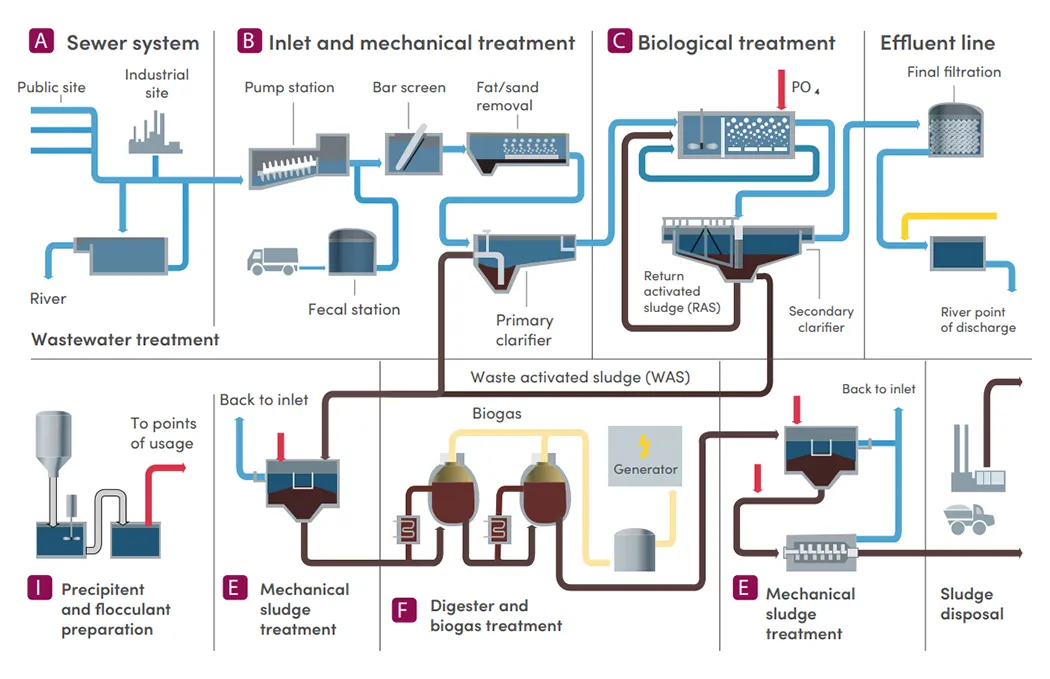
Wastewater treatment
Pretreatment
It is called pretreatment because it is the prelude to the purification treatment that the wastewater will receive. This process fulfills the functions of regulating and measuring the flow of water that enters the plant. In addition, this treatment removes large floating solids, sand and grease present in the sewage.
These undesirable agents are eliminated through a filtration process, this being essential for the correct development of this stage. In this process, wastewater is prepared to facilitate such treatment. This in order to protect the installation and avoid damage to the equipment used in the different operations and processes that make up the treatment system.
Primary treatment
The objective of this treatment is the elimination of suspended solids. This is done through a simple sedimentation process by gravity or assisted by chemical substances. The residual water is deposited in large settling tanks and is retained there for 1 to 2 hours.
This treatment consists of a set of physicochemical methods that are applied in order to reduce the level of contamination and the content of suspended particles in the water. These suspended particles can be floating or settleable. Depending on the objective to be achieved, a filter or flotation system is used.
Among the methods used in this first wastewater purification treatment are:
Sedimentation
It is the process by which particles sink to the bottom due to the action of gravity. Up to 40% of solids that water contains can be removed. This process is carried out in tanks called decanters.
Floatation
It is based on removing the fats,
foams and oils found in the surface layer of water due to their low density.
Likewise, low-density particles can be eliminated, for this air bubbles are injected, which facilitates their ascension. With this method, up to 75% of the suspended particles can be removed. This process takes place in other tanks called dissolved air floats.
Neutralization
It lies in the normalization of the pH, in other words, adjusting it to the value of water, which is typically in the range of 6-8.5. In the case of acid wastewater (low pH) such as those containing heavy metals, alkaline substances (high pH) are added to increase the pH of water. In alkaline wastewater, on the other hand, CO2 is often used to lower the pH of water to normal values.
Secondary treatment
The main objectives of this stage is to eliminate organic matter in a colloidal state and in dissolution through an oxidation process of biological nature. Also, the degradation of substances of the biological content present in the wastewater caused by human waste.
Within this treatment, various aerobic and anaerobic processes are carried out.
Aerobic
They are carried out in the presence of oxygen, and it is essential to introduce it into the tanks where the wastewater is found. During this stage, part of the degradation of organic matter takes place, from which CO2 and water are released. The elimination of highly toxic nitrogen products also occurs, in a reaction called nitrification it is transformed into nitrate. For its part, nitrate, despite not being toxic, is an assimilable form of nitrogen. This could cause a spread of algae, as well as nutrient enrichment of the water in the receiving environment. Through denitrification it is converted to nitrogen and released into the atmosphere.
Anaerobic
They are carried out in the absence of oxygen. During this process, fermentative reactions take place where organic matter is transformed into energy, carbon dioxide and methane. Some of the aerobic and anaerobic methods of wastewater treatment are:
Active sludge
This aerobic process consists of adding lumps or flocs of organic matter with microorganisms to the wastewater and constantly infiltrating oxygen to produce reactions.
Green filters
They are crops that are irrigated with wastewater, because they have the ability to absorb their compounds.
Bacterial beds
It is an aerobic process, which consists of supports where the microorganisms are. The residual water is thrown in small amounts to maintain aerobic conditions.
Anaerobic digestion
It is an anaerobic process that is carried out in completely closed tanks. Mainly used are bacteria that produce methane and acid when they degrade organic matter.
Tertiary treatment
This is the final stage of wastewater treatment. A series of processes are carried out in it, including the elimination of pathogenic agents such as fecal bacteria and nutrients. These processes increase the quality of water to be discharged into seas, rivers, lakes and other hydrographic basins to required standards.
Next, the different processes that are carried out in the treatment of wastewater with the aim of reducing and eliminating the concentrations of dissolved matter present in them will be described:
Precipitation
Precipitation consists of the subtraction of the dissolved substance present in the water, through the addition of reagents that form an insoluble compound with it, thus facilitating its removal by any of the methods of elimination of suspended matter. The most frequent reagent to carry out this procedure is Ca2+ since this compound has coagulating characteristics, which causes the use of this compound in both urban and industrial wastewater treatment.
Filtration
This technology is primarily used to remove suspended solids from water supplies using porous materials. These solids may consist of dirt, silt, or other particles that may interfere with the intended use of the water or a downstream treatment technology.
Electrochemical processes
Electrochemical processes, as their name indicates, are based on the use of electrochemical techniques, where an electric current through an electrolyte passes through the wastewater, generating oxidation-reduction reactions both at the cathode and at the anode. The main advantage of this method is the absence of the use of reagents and that this method controls the potential of the electrode, allowing to select the dominant electrochemical reaction that the resource requires for its treatment.
Ion Exchange
Ion exchange uses a material, known as ion exchange resins, which selectively retains the ions dissolved in the wastewater on its surface, keeps them temporarily attached to the surface, and transfers them to a regenerating solution. Ion exchange is usually used to remove salts when they are in low concentrations, its application being usual for the demineralization and softening of water, as well as the retention of certain chemical products and the demineralization of sugar syrups.
Disinfection
The use of disinfectants in wastewater treatment seeks to produce water free of pathogens or living organisms that can contaminate water sources, avoid the production of undesirable by-products in disinfection and maintain the bacteriological quality in the subsequent conduction network. Some of these methods are: