CIP/SIP Process Efficiency (Cleaning/Sterilization in place)
The processes of cleaning and/or sterilization in place (CIP or SIP) are a priority in the production of food as health products. The efficient operation of these systems ensures compliance with cleaning regulations and the time of machinery use and production processes.
CIP process piping and instrumentation diagram
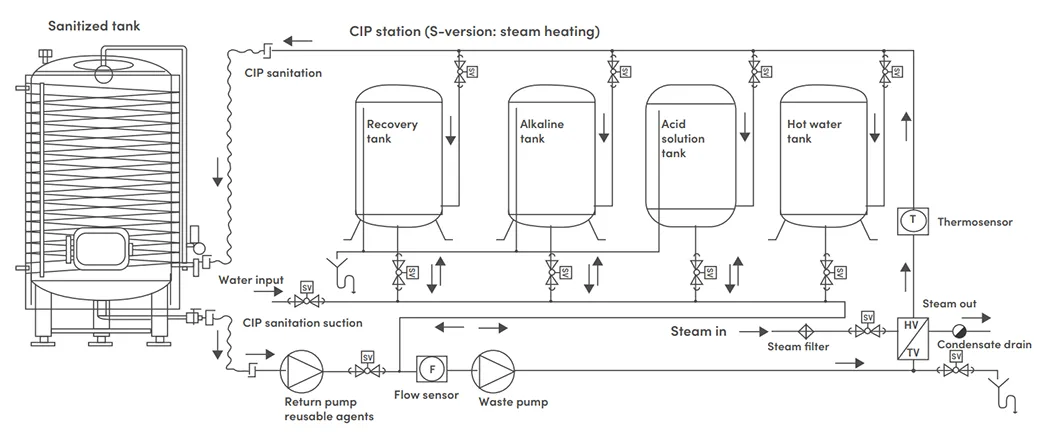
CIP & SIP Automated system
The automation of the operation in a CIP system guarantees strict compliance with cleaning standards, obtaining savings in energy consumption and chemical products, as well as optimizing the duration of this process, allowing the availability of production machinery to be increased.
Benefits of automating the CIP process:

HMI Process Screen
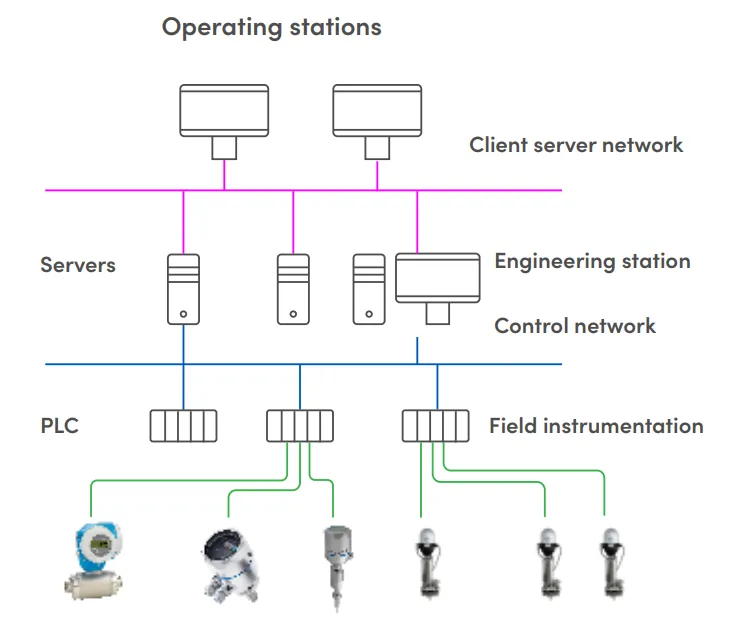
CIP Control architecture
CIP Process description:
Phase 1
Clean water is pushed through in order to eject all product from the line to be cleaned
Phase 2
A rinse is carried out with recovered water, this water is a solution of water + soda obtained from the rinse after the recirculation phase with soda; with the benefit that allows us to make a first pass through the circuit with a solution with a higher cleaning power than water and allows us to save water and soda.
Phase 3
A recirculation of water and soda is done with a concentration of 2-4% during the set time.
Phase 4
Rinsing with network water is done, gathered from the retrieved water deposit and that will help us in the first rinse of the next cleaning.
Phase 5
A recirculation of acid solution is done with a required concentration (depending on the used acid) during the set time.
Phase 6
Rinsing with network water is done, gathered from the retrieved water deposit and that will help us in the first rinse of the next cleaning.
Phase 7
This is the sterilization phase (SIP) that can be done by recirculation of steam or some sterilization solution.
Automatic CIP system
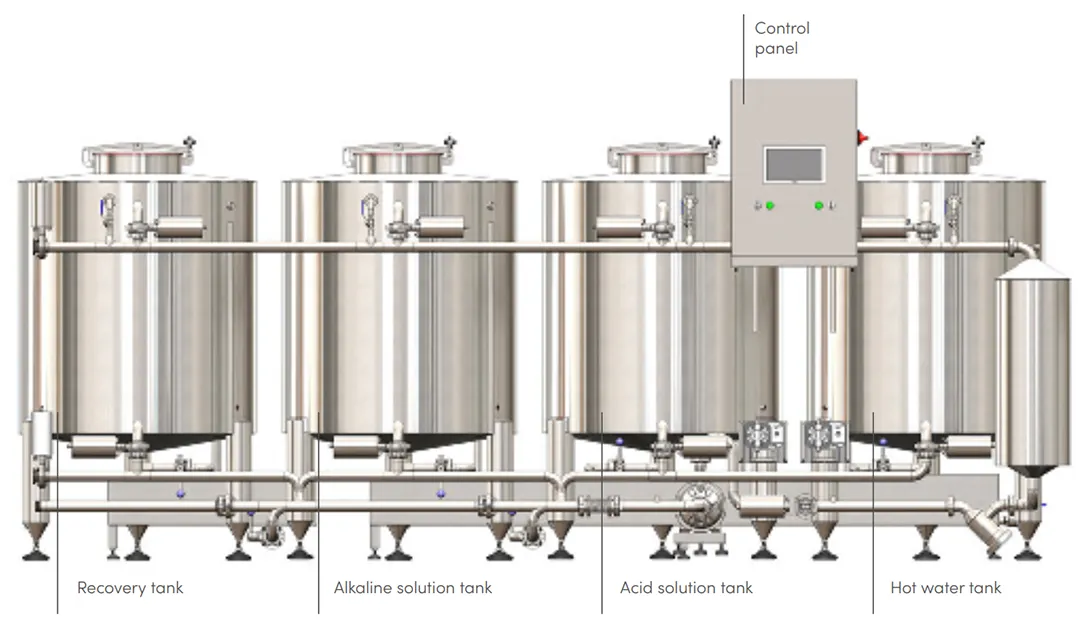

Measurement and control elements
To guarantee complete cleaning, four factors must be taken into account that combine with each other: mechanical action, chemistry, temperature and time. These four elements are what make up the so-called Sinner circle and can be monitored through instrumentation and control.
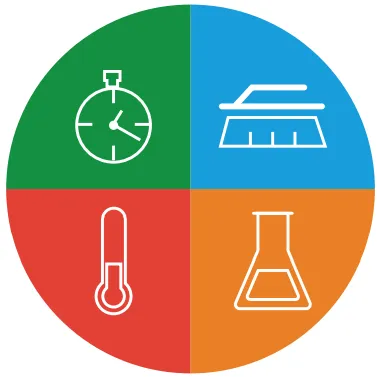
Sinner cleaning circle

Chemical product
Chemical cleaning

Conductivity transmitter for detergent concentration measurement

Mechanical energy
Flow meter

Flow meter to ensure minimal speed and cleaning agent recirculation

Temperature
Temperature meter

Temperature meter for an efficient cleaning agent reaction

Time
Automatic valve

Automatic butterfly hygienic valve for cut offs among phases.