Food in general
The processed food industry is highly competitive. Some aspects that influence this industry may be: Price lowering, changes in products due to commercial strategies, and the changes in the consumer preferences. Therefore, everyday companies face the challenge of improving their processes, quality and savings in energy consumption.
General services
The food industry needs general services produced effciently to be used in production processes, the most common services are the following:
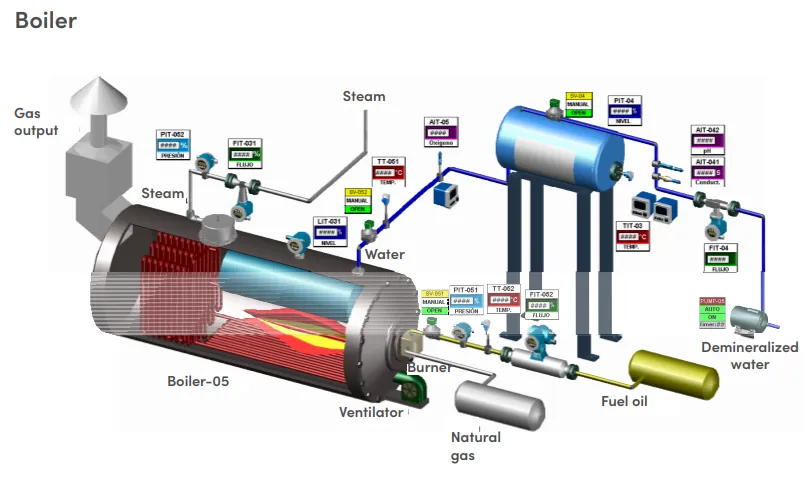
Steam generation process
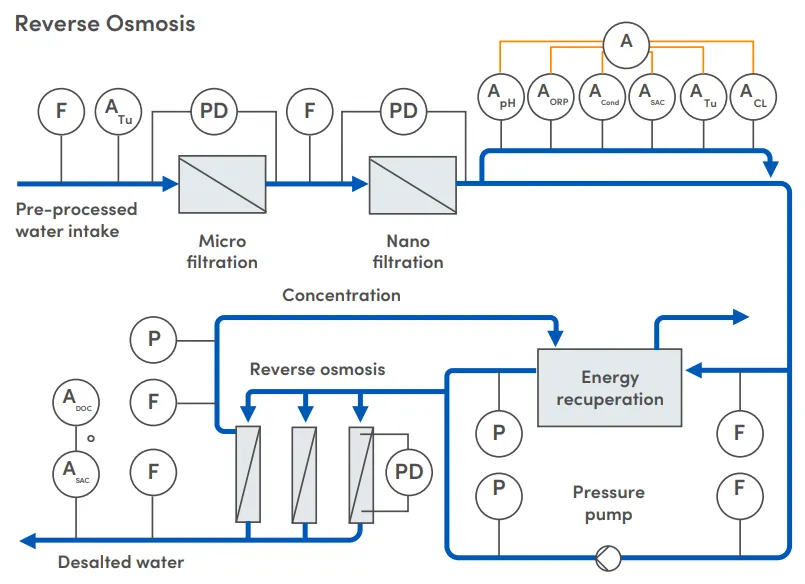
Reverse osmosis process for water treatment
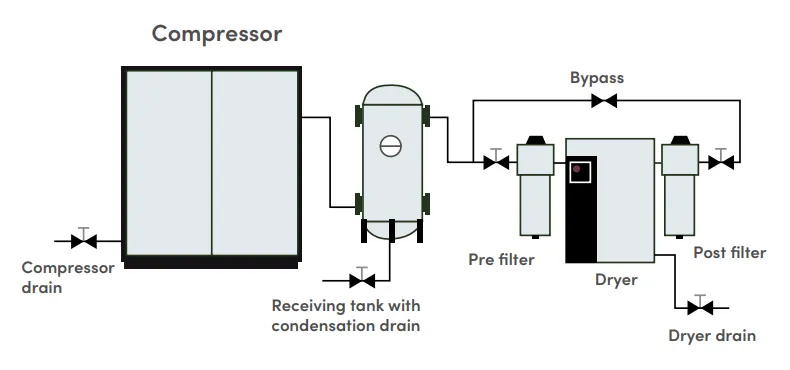
Compressed air cycle
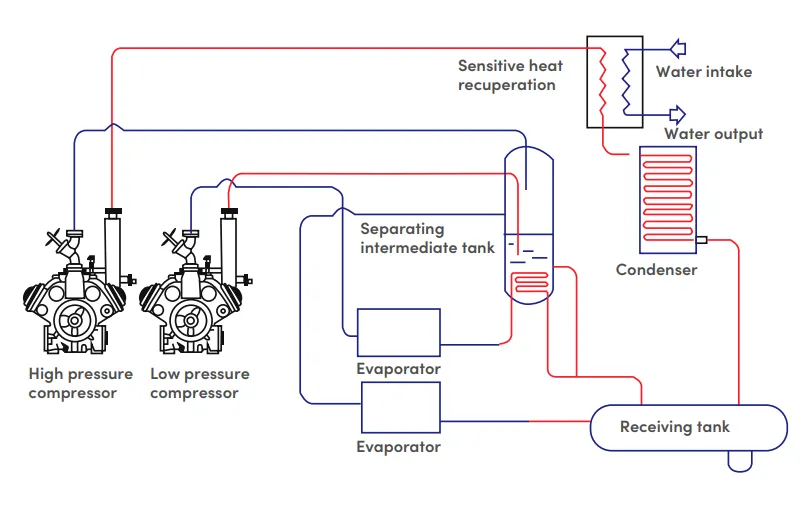
Cooling system via ammonia
Cooking oil production
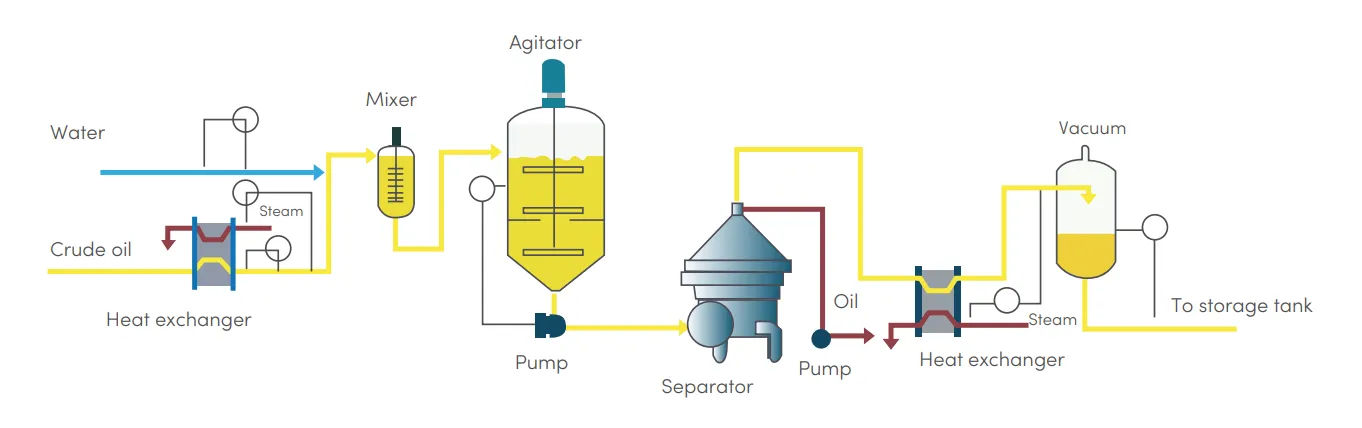
Cooking oil production
Degumming of oil is the first step in an oil refining plant and is essential in the refining of vegetable oil. It can be done by hydration. Degumming of oil by hydration consists of adding hot water since impurities like phosphatides, gums and proteins are soluble in oil, but insoluble in water. That way, impurities can be separated.
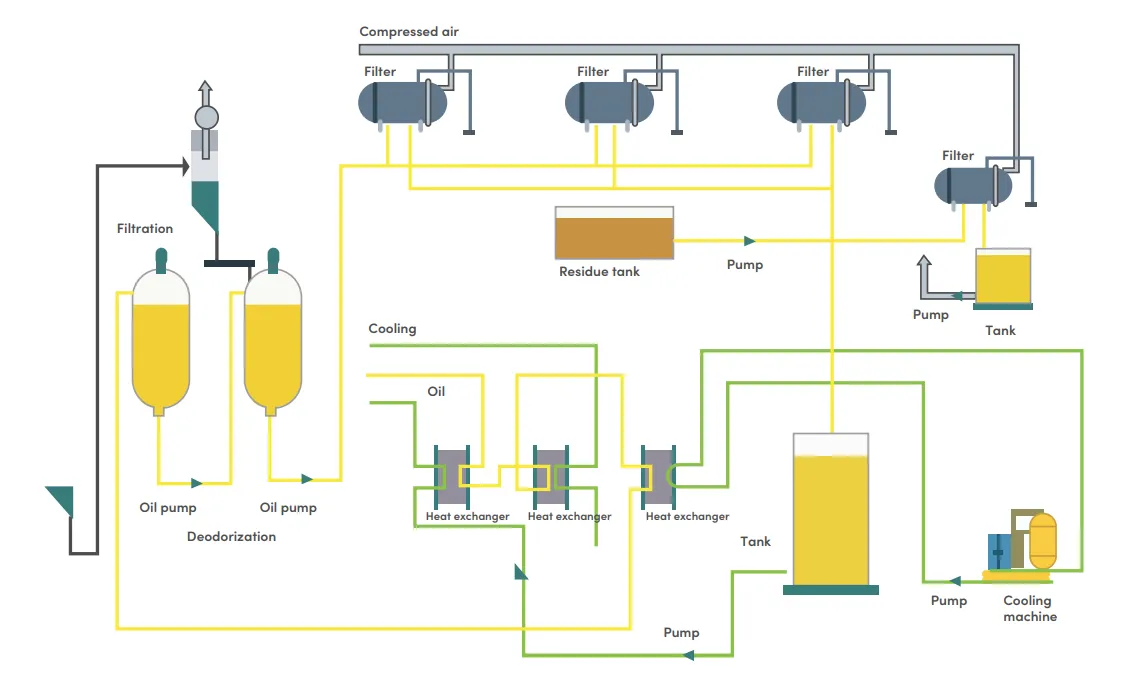
Vegetable oil refinery
All vegetable oil refineries operate under the same basic principles. Crude oil is obtained from an ejector or a solvent extraction plant, since it has impurities that must be eliminated for the oil to be edible, more digestible and more stable for its storage. This impurity elimination process is called refining.
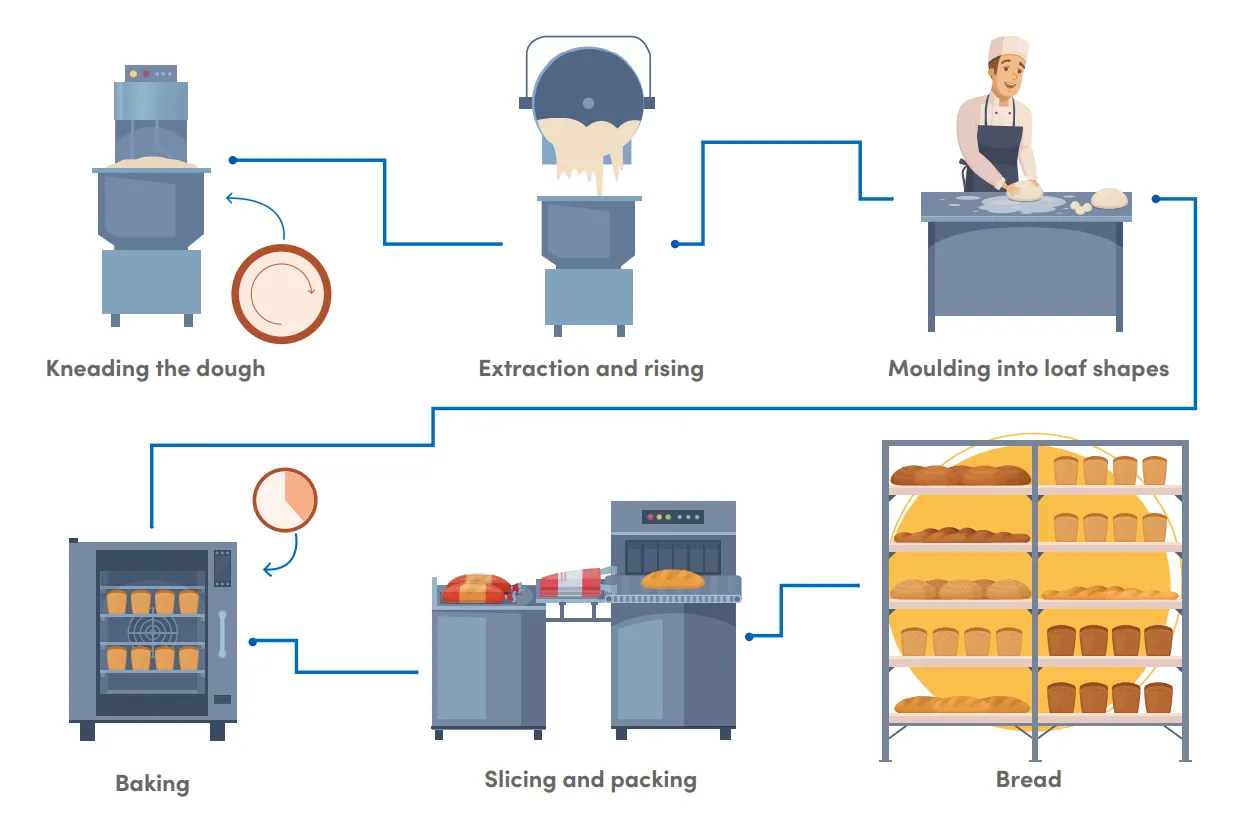
Baking Industry
Baking Industry
In the baking industry there are a lot of methods, which vary depending on the type of bread, its characteristics, the equipment and raw material involved in the process
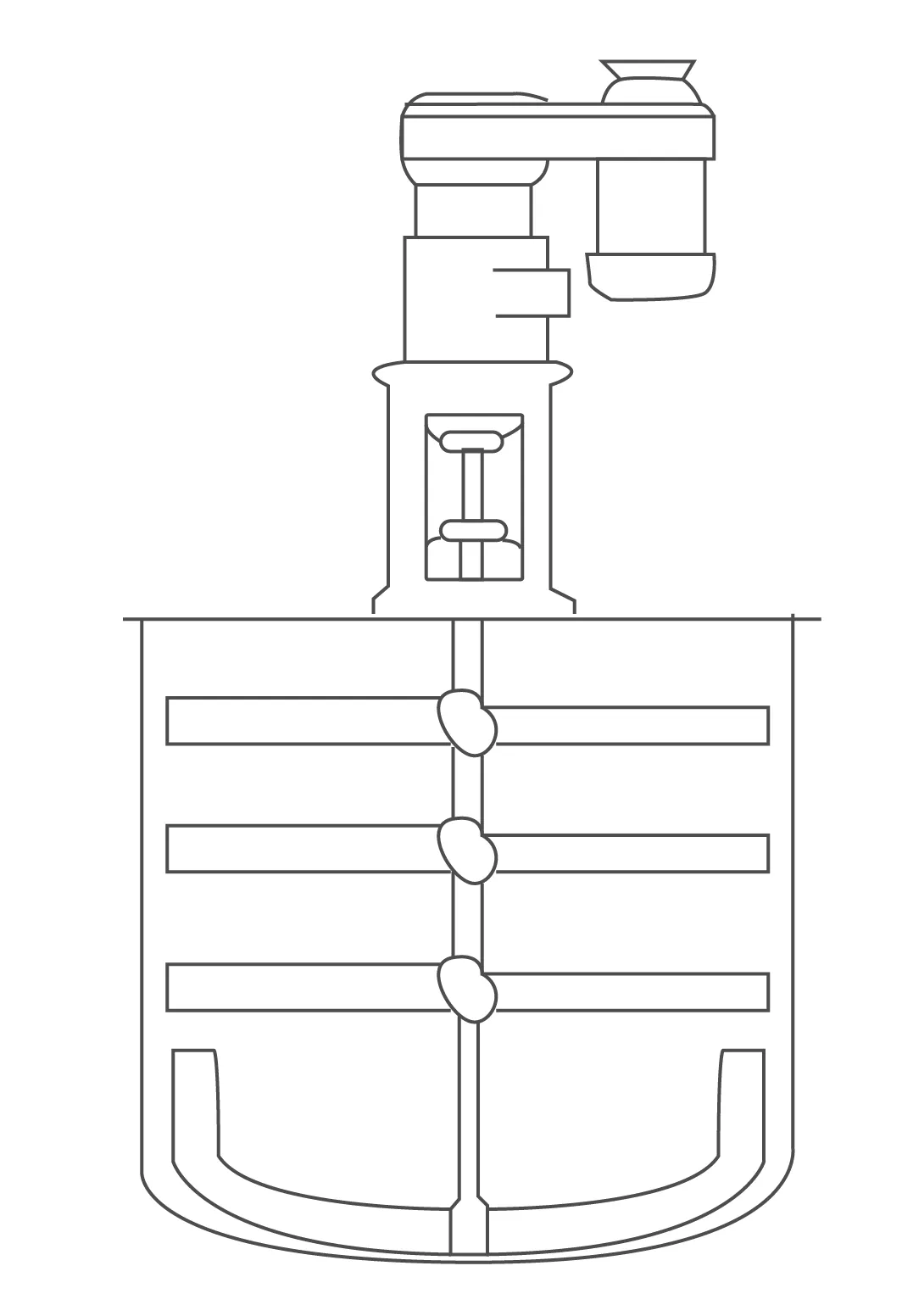
Mixture and primary fermentation
There are two stages in the mixture process: the first one is to incorporate the ingredients, the second is the mass structure development, also known as gluten net.
It is at this point that yeast starts doing its job, transformation of sugar into carbon dioxide and organic acids. Every mass has a different primary fermentation time, depending on its formulation.
Baking and cooling
Lean dough like the one used in baguettes or dough made without any fats, sugar, eggs, etc. tend to use the oven at very high temperature ranging from 450 to 475 °F (230 °C-250°C). Enriched bread such as sweet bread is baked from 350 to 400 °F (180 °C – 200 °C). In most cases, smaller bread must be in the oven at a higher temperature than a bigger one; therefore one must pay attention to its color during the baking process.
After bread has been taken out of the oven, it still has an excess of moisture and carbon dioxide. Bread needs time to cool so that moisture and gas dissipate. After cooling, texture, flavor and smell become what they are supposed to.